Managerial Strategies
Table of Contents
Managerial strategies refer to the deliberate plans and actions implemented by managers to achieve organisational objectives efficiently. These strategies include resource allocation, goal setting, and team management to maximise productivity and ensure long-term sustainability.
Resource Allocation:
One critical aspect of strategic management involves the reasonable allocation of resources within an organisation. Resources can include financial capital, human capital, time, equipment, and materials. Effective managers analyse the organisation’s needs, assess the availability of resources, and allocate. them strategically to different projects, departments, or initiatives. By allocating resources efficiently, managers ensure that the organisation operates optimally, avoiding wastage and maximising available resources. This strategic allocation contributes to cost-effectiveness, enhances productivity, and facilitates the achievement of organisational goals.
Goal Setting:
Another crucial aspect of managerial strategies involves goal setting. Goals offer precise organisational guidance and serve as milestones for assessing advancement. Managers collaborate with key stakeholders to define SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-bound) goals that align with the organisation’s mission and vision. These goals may encompass various aspects, such as financial targets, market share objectives, customer satisfaction goals, or innovation milestones. By setting clear and actionable goals, managers provide focus and motivation for employees, fostering a sense of purpose and direction within the organisation. Moreover, goal setting facilitates practical performance evaluation and decision-making, enabling managers to steer the organisation towards long-term success.
Team Management:
Effective team management is essential for realising organisational objectives and maintaining a cohesive workforce. Managers play a pivotal role in assembling, developing, and leading teams towards shared goals. This involves recruiting and selecting talent, fostering a positive work culture, promoting collaboration, and providing support and guidance to team members. Effective communication, conflict resolution, and performance feedback are also integral to team management. By nurturing high-performing teams, managers cultivate a productive and engaged workforce, driving innovation, creativity, and organisational success. Strong team management practices also contribute to employee satisfaction, retention, and overall organisational resilience.
In summary, managerial strategies encompass a multifaceted approach that addresses critical aspects such as resource allocation, goal setting, and team management. Managers aim to maximise productivity, foster innovation, and ensure long-term sustainability by focusing on these vital areas. Through strategic planning, effective leadership, and continuous improvement initiatives, managers are pivotal in steering the organisation towards success in today’s dynamic and competitive business landscape.
Tasks And Strategies For Successful Restaurant Operations Management
Importance of Managerial Strategies
Effective managerial strategies are essential for driving organisational growth and maintaining competitive advantage in today’s dynamic business landscape. By aligning resources, capabilities, and goals, managers can optimise performance, mitigate risks, and capitalise on emerging opportunities, fostering innovation and continuous improvement.
- Optimising Performance:
When managers align resources, capabilities, and goals, they ensure that the organisation’s resources are directed towards achieving its strategic objectives. By carefully allocating resources based on the organisation’s capabilities and the requirements of its goals, managers can optimise performance across various functions and departments. This alignment helps streamline workflows, reducing inefficiencies and enhancing overall productivity. For instance, if the objective is to boost sales, managers assign resources to marketing campaigns, sales training initiatives, and customer relationship management systems. This allocation aims to enhance the sales team’s performance and improve outcomes.
- Mitigating Risks:
Efficient alignment of resources, capabilities, and goals empowers managers to identify and address risks more effectively. By comprehending the organisation’s strengths and weaknesses, managers can evaluate potential risks linked with pursuing specific objectives and proactively counter them. For example, if the aim is to enter a new market, managers might conduct extensive market research to grasp the competitive scenario and pinpoint potential obstacles or hurdles to entry. They can then develop risk mitigation strategies such as diversifying product offerings, partnering with local distributors, or establishing contingency plans to mitigate potential losses or setbacks.
- Capitalising on Emerging Opportunities:
Moreover, aligning resources, capabilities, and goals empowers managers to seize emerging opportunities in the market. By remaining vigilant to shifts in the external environment and grasping the organisation’s internal strengths, managers swiftly pinpoint opportunities that align with the company’s strategic goals. For instance, if there’s a rising demand for sustainable products, managers can redirect resources towards research and development endeavours to create eco-friendly product lines or improve existing offerings to meet this demand. By seizing these opportunities, managers can gain a competitive edge and drive growth and innovation within the organisation.
- Fostering Innovation and Continuous Improvement:
Finally, aligning resources, capabilities, and goals nurtures a culture of innovation and ongoing organisational enhancement. By encouraging cross-functional collaboration, promoting knowledge sharing, and empowering employees to take calculated risks, managers can inspire creativity and drive innovation at all levels of the organisation. Moreover, by setting ambitious yet achievable goals and providing the necessary resources and support, managers motivate employees to strive for excellence and continuously seek ways to improve processes, products, and services. This innovation and continuous improvement culture enhances the organisation’s competitive position and ensures its long-term sustainability in a rapidly changing business landscape.
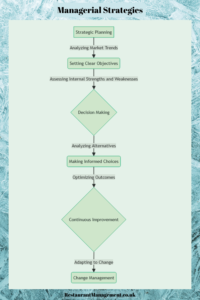
Components of Effective Managerial Strategies
Strategic Planning
Strategic planning forms the foundation of managerial strategies, providing a roadmap for achieving organisational goals. It involves analysing market trends, assessing internal strengths and weaknesses, and setting clear objectives that guide decision-making and resource allocation.
Let’s elaborate on how strategic planning forms the foundation of managerial strategies and why it’s essential for achieving organisational goals:
- Providing a Roadmap for Achievement:
Strategic planning acts as the guiding force that directs the organisation toward its intended destination. It involves a structured approach to setting objectives, evaluating resources, and mapping out a path to accomplish long-term goals. Strategic planning ensures that all business members understand their roles and responsibilities in advancing the overarching objectives by creating a clear roadmap. This clarity of direction enables managers to align efforts, prioritise tasks, and allocate resources effectively, thereby enhancing the organisation’s chances of success.
- Analysing Market Trends:
A crucial aspect of strategic planning is the analysis of market trends and dynamics. Managers must be alert to the external environment, including shifts in consumer preferences, technological advancements, regulatory changes, and competitive landscapes. By conducting thorough market research and trend analysis, managers can identify emerging opportunities and potential threats that may impact the organisation’s performance. This informed understanding of market trends enables managers to make strategic decisions regarding product development, market positioning, and expansion strategies, thereby increasing the organisation’s competitiveness and market relevance.
- Assessing Internal Strengths and Weaknesses:
In addition to external factors, strategic planning involves a comprehensive assessment of the organisation’s strengths and weaknesses. Managers must critically evaluate the organisation’s financial health, operational capabilities, human resources, technological infrastructure, and brand reputation. By identifying internal strengths that can be leveraged and weaknesses that need to be addressed, managers can develop strategies to capitalise on competitive advantages and overcome challenges. This reflective analysis enables managers to make informed decisions about resource allocation, capability development, and organisational restructuring, enhancing the organisation’s resilience and agility in the face of change.
- Setting Clear Objectives:
Central to strategic planning is setting clear and achievable objectives that guide decision-making and resource allocation. Objectives should be specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART), providing a tangible framework for evaluating progress and success. By defining clear objectives, managers provide direction and focus for the organisation, aligning efforts towards common goals. Moreover, clear objectives facilitate effective performance management, enabling managers to track performance metrics, identify deviations from the plan, and make necessary adjustments in real time. This iterative process of goal setting and performance evaluation ensures that the organisation remains adaptive and responsive to changing circumstances, ultimately enhancing its ability to achieve long-term success.

Related article:
How To Make A Profit In Your Restaurant
Restaurant Management Structure
Leadership and Team Management
Strong leadership are crucial for inspiring and guiding teams towards common objectives. Managers must cultivate a positive work culture, foster collaboration, and empower employees to unleash their full potential. Effective communication, coaching, and performance feedback are vital for building high-performing teams and driving results.
- Inspiring and Guiding Teams:
Strong leadership is essential for inspiring and guiding teams towards shared objectives. Leaders set the tone for the organisation by articulating a compelling vision, motivating employees, and leading by example. They provide clarity of purpose, instil confidence, and rally teams around common goals. Through their vision and passion, leaders inspire commitment and dedication, driving individuals to go above and beyond in pursuit of excellence.
- Cultivating a Positive Work Culture:
Managers are crucial in nurturing a positive work environment that encourages collaboration, creativity, and mutual respect. A positive work culture fosters employees’ sense of belonging and pride, leading to higher morale, engagement, and productivity. Managers can promote a positive work culture by encouraging open communication and recognising and celebrating achievements.
- Empowering Employees:
Influential leaders empower employees to unleash their full potential by providing autonomy, support, and opportunities for growth and development. Empowered employees feel trusted and empowered to take ownership of their work, make decisions, and contribute meaningfully to the organisation. Managers can empower employees by delegating authority, providing resources and training, and creating avenues for feedback and recognition. Managers tap into their creativity, innovation, and problem-solving abilities by empowering employees and driving continuous improvement and organisational success.
- Effective Communication, Coaching, and Feedback:
Communication, coaching, and feedback are essential to effective leadership and team management. Managers must communicate clearly and transparently, ensuring that information flows freely within the organisation and teams understand their roles and responsibilities. Moreover, managers must offer coaching and mentorship to support employees in skill development, overcoming challenges, and realising their full potential. Regular feedback and performance evaluations are vital for identifying strengths, addressing weaknesses, and fostering growth and development. Managers motivate and inspire employees by providing constructive feedback and recognition, driving high performance and results.
Decision-Making and Problem-Solving
Managers often encounter complex challenges that require quick and effective decision-making. By employing analytical tools, critical thinking, and risk assessment techniques, they can evaluate alternatives, anticipate outcomes, and make informed choices that optimise outcomes and minimise potential risks.
- Utilising Analytical Tools:
Managers leverage analytical tools to gather and analyse data, extract insights, and inform decision-making processes. These tools include financial analysis software, market research reports, performance metrics dashboards, and predictive modelling techniques. By harnessing the power of data analytics, managers gain a deeper understanding of the problem at hand, identify trends and patterns, and assess the potential impact of different courses of action. Analytical tools enable managers to make data-driven decisions grounded in empirical evidence, thereby increasing the likelihood of success and minimising uncertainty.
- Applying Critical Thinking:
Critical thinking is a fundamental skill managers employ when facing complex challenges. It involves systematically analysing information, questioning assumptions, and evaluating alternative perspectives to arrive at well-reasoned conclusions. Managers engage in critical thinking by breaking down complex problems into manageable components, identifying underlying causes and implications, and weighing the pros and cons of different options. By promoting a culture of critical thinking among their teams, managers foster creativity, innovation, and efficient problem-solving, empowering the organisation to adapt and prosper.
- Conducting Risk Assessment:
Effective decision-making requires managers to assess and manage risks effectively. Managers employ risk assessment techniques to identify potential threats, evaluate their likelihood and impact, and develop strategies to mitigate or avoid them. This involves conducting scenario analyses, sensitivity assessments, and probabilistic modelling to anticipate potential outcomes and associated risks. By proactively addressing risks, managers can minimise potential disruptions, safeguard organisational assets, and capitalise on opportunities with favourable risk-reward profiles. Moreover, risk assessment fosters a culture of risk awareness and preparedness within the organisation, enabling managers and employees to make informed decisions and navigate uncertainties confidently.
Change Management
In today’s dynamic business environment Managers must adapt to evolving market conditions, technological advancements, and consumer preferences. Effective change management involves proactive planning, stakeholder engagement, and communication strategies to facilitate smooth transitions and minimise disruptions.
- Adapting to Evolving Market Conditions:
Managers operate in dynamic market environments with shifting economic conditions, competitive landscapes, and regulatory frameworks. To remain competitive and sustainable, managers must stay attuned to market trends, emerging opportunities, and potential threats. This entails continually monitoring, analysing, and employing strategic foresight to anticipate and effectively respond to changes in customer needs, industry dynamics, and market forces. By adapting their strategies, products, and operations in response to evolving market conditions, managers can capitalise on growth opportunities and mitigate risks of obsolescence or stagnation.
- Embracing Technological Advancements:
Technological advancements are transforming industries and reshaping business models at an unprecedented pace. Managers must embrace technological innovations and leverage them to enhance operational efficiency, improve customer experiences, and drive innovation. This entails investing in new technologies, such as artificial intelligence, automation, data analytics, and digital platforms, and integrating them into business processes and workflows. By leveraging the capabilities of technology, managers can discover fresh avenues for expansion, optimise operations, and attain a competitive advantage in the market.
- Responding to Consumer Preferences:
Consumer preferences and behaviours constantly evolve in response to changing societal trends, demographic shifts, and cultural influences. Managers must stay attuned to these shifts and adapt their products, services, and marketing strategies accordingly. This may involve conducting market research, gathering customer feedback, and analysing consumer data to understand changing preferences and anticipate future trends. By promptly addressing consumer preferences, managers can improve customer satisfaction, foster brand loyalty, and sustain a competitive edge in the market.
- Implementing Effective Change Management:
Effective change management is essential for guiding organisations through transition and transformation. It involves proactive planning, stakeholder engagement, and communication strategies to facilitate smooth transitions and minimise disruptions. Managers must communicate the rationale for change, outline clear objectives and expectations, and address stakeholder concerns and resistance. Managers foster a sense of ownership and dedication by engaging employees in the process of change, seeking their input, and offering support and resources, facilitating the organisation’s ability to adjust rapidly and efficiently to new circumstances. Additionally, effective change management ensures that changes are implemented in a structured and systematic way, minimising risks of confusion, resistance, or productivity losses.
Conclusion
Effective managerial strategies are instrumental in navigating the complexities of today’s business landscape and achieving sustainable growth. By embracing strategic planning, leadership development, and continuous improvement, managers can drive organisational excellence and outperform competitors in the dynamic marketplace. Empower your managers with the knowledge, skills, and resources they need to thrive in their roles and lead your organisation towards a prosperous future.
FAQs:
What are the four management strategies?
The four main management strategies encompass various approaches to achieving organisational goals. These include strategic planning, which involves setting long-term objectives and determining how to achieve them; resource allocation, which consists of distributing resources effectively to support strategic goals; team management, which involves building and leading teams to execute strategies; and decision-making, which consists in making informed choices to address challenges and opportunities.
What is an example of managerial strategy?
An example of a managerial strategy could be implementing a cost leadership strategy in a manufacturing company.
This approach prioritises the production of goods or services with minimal costs while ensuring with satisfactory quality standards. Managers can attain this objective by streamlining production procedures, securing advantageous supplier agreements, and reducing unnecessary waste. By proficiently executing this managerial approach, the company endeavours to enhance its competitive edge by providing offerings at more economical prices compared to its rivals.
What are the five categories of strategic management?
The five types of strategic management include the following:
- Corporate-level strategy refers to the decisions made by an organisation regarding its overall scope and direction.
- Business-level strategy pertains to a business unit’s competitive approach within a specific industry or market segment.
- Functional-level strategy refers to decisions made within individual functional areas, such as marketing, operations, or finance.
- Global strategy refers to businesses’ methods and tactics to expand and compete in international markets. It involves exploring new markets, identifying opportunities, and creating effective plans to gain a competitive advantage.
- Competitive strategy involves positioning the organisation to gain an advantage over competitors.
What is the primary managerial strategy?
A fundamental approach to management is strategic planning, which involves a comprehensive process of defining an organisation’s mission, vision, and objectives, analysing both internal and external environments, developing strategies to achieve predetermined goals, and executing and monitoring these strategies. It serves as the roadmap for the organisation, guiding decision-making and resource allocation to ensure alignment with overarching objectives. Effective strategic planning drives organisational success and maintains competitiveness in today’s dynamic business landscape.
Unlock the Five Secrets to Successful Restaurant Management Strategies
https://restaurantmanagement.co.uk/?s=management+strategies

