First Published: 17 December 2022
Everything You Need To Know About Inflation
What is inflation?
How to minimise the inflation effect on your restaurant without leading to closure is at the forefront of every restaurant owner at this moment. So what is inflation? Inflation is a general rise in prices across many markets and goods. It can be caused by several factors, such as increased production, increasing demand, or higher costs of raw materials.
This happens when the quantity of money (or currency) in circulation increases faster than the rate at which people are able to purchase goods and services.
When inflation reaches a certain level, it becomes difficult for people to afford basic needs like food and shelter without growing their incomes significantly.
When inflation starts to exceed wage growth, businesses start to face challenges because they cannot pay employees their increased salaries with inflated purchasing power. In turn, this can lead to reduced consumer spending, decreased production, and even business closures. It’s important for restaurant managers to be aware of how inflation affects their daily lives so that they are prepared for any potential consequences.
In the long run, elevated levels of inflation lead to decreased purchasing power for money and damaging economic outcomes such as decreases in investment spending and wages. Furthermore, it’s important to monitor inflation rates so you can make informed decisions about your restaurant’s financial future.

What are the four effects of inflation on restaurant businesses?
Inflation has a tremendous impact on the food industry, directly affecting food prices and availability as well as the overall cost of running a restaurant.
Additionally, it negatively impacts businesses by limiting their ability to raise prices, as well as making other costs (such as wages) rise faster than inflation.
Here are four ways in which inflation affects restaurants:
- Food ingredients and equipment become scarce due to rising demand, pushing up prices. Menu choices become much narrower as ingredient availability diminishes
- Higher food prices mean that customers have less money left over to spend at restaurants. Restaurants must increase menu items or charge more for basic dishes in order to make ends meet. Higher food costs lead to increased menu price points, which forces customers to ask for higher minimum wage increases BEFORE they even consider eating out because it’s simply unaffordable at many establishments.
- Rising insurance premiums eat away at restaurateurs’ profits – even if claims don’t exceed normal levels.
- Inflation erodes the value of currency over time – meaning that receipts from previous years no longer buy as much. Restaurants receive less revenue due to limited consumer spending power – high food prices cause people who live on tight budgets or earn lower wages not only to skip meals altogether but also dine out less frequently than they would like.
In order for restaurants to offset these losses, their margins must increase dramatically (leading them towards some unethical business practices) or expenses must be cut elsewhere within the business. Overall profitability declines as cost-of-living pressures put further stress on management

How Does Inflation Affect The Food Industry?
What are the consequences for Restaurant businesses when inflation occurs?
Restaurant businesses have to contend with several different challenges, including high food costs, rising labour prices, and increased maintenance costs. Inflation can make all of these challenges even harder for restaurateurs to manage.
For example, when the cost of food goes up faster than wages or rent increases, restaurant owners are forced to raise menu prices in order to recoup their losses. This often leads to higher customer bills (and decreased profits), not just at restaurants that serve expensive items like steak and lobster, but at those that serve cheaper fare as well.
How inflation impacts restaurant businesses negatively
There are a number of ways in which inflation impacts restaurant businesses negatively. One such way is through its impact on diners’ discretionary income. As wage earners see their take-home pay shrink while prices continue going up throughout the economy overall:
- They’re less likely than ever before to spend money out at restaurants—even if those restaurants offer relatively low menu pricing compared with other dining options.
- This downward spiral creates major difficulties not only for individual restaurateurs but also for the entire industry as a whole; it’s estimated that each 1% increase in price inflation reduces total U.K.-based retail sales by about 0.5%.
How can hospitality companies tough out inflation?
Hospitality companies can tough out inflation by ensuring that:
- Their menus and prices remain stable, while also reducing their operating costs. By doing this, they will be able to keep their customers happy and content even as food prices continue to increase.
- Also, by pricing their menu using fixed-price methods. A fixed-price menu is one that has a set price for a full meal. Most of the time, that means diners get an appetiser, a main dish, and a dessert. For each of the three courses, diners can choose from different options, but the price stays the same no matter what they choose. This allows the restaurant to maintain its margins even as prices rise, and it also makes it difficult for customers to switch to cheaper alternatives.
- Another strategy that restaurant businesses can employ is increasing the amount of promotional activity undertaken in order to attract new customers. This will help offset any increases in food expenses and make up for lost revenue due to price hikes.
- Additionally, restaurant owners should consider using technology platforms such as online ordering or mobile apps to improve customer engagement and experience.
- Other measures that may be taken include increasing investment in new technology to increase efficiency or introducing more innovative menu items.
Restaurant owners should always be prepared to adapt their strategies if necessary in order to keep up with changing trends.

Restaurant Inflation in the UK
How bad is restaurant inflation in the UK?
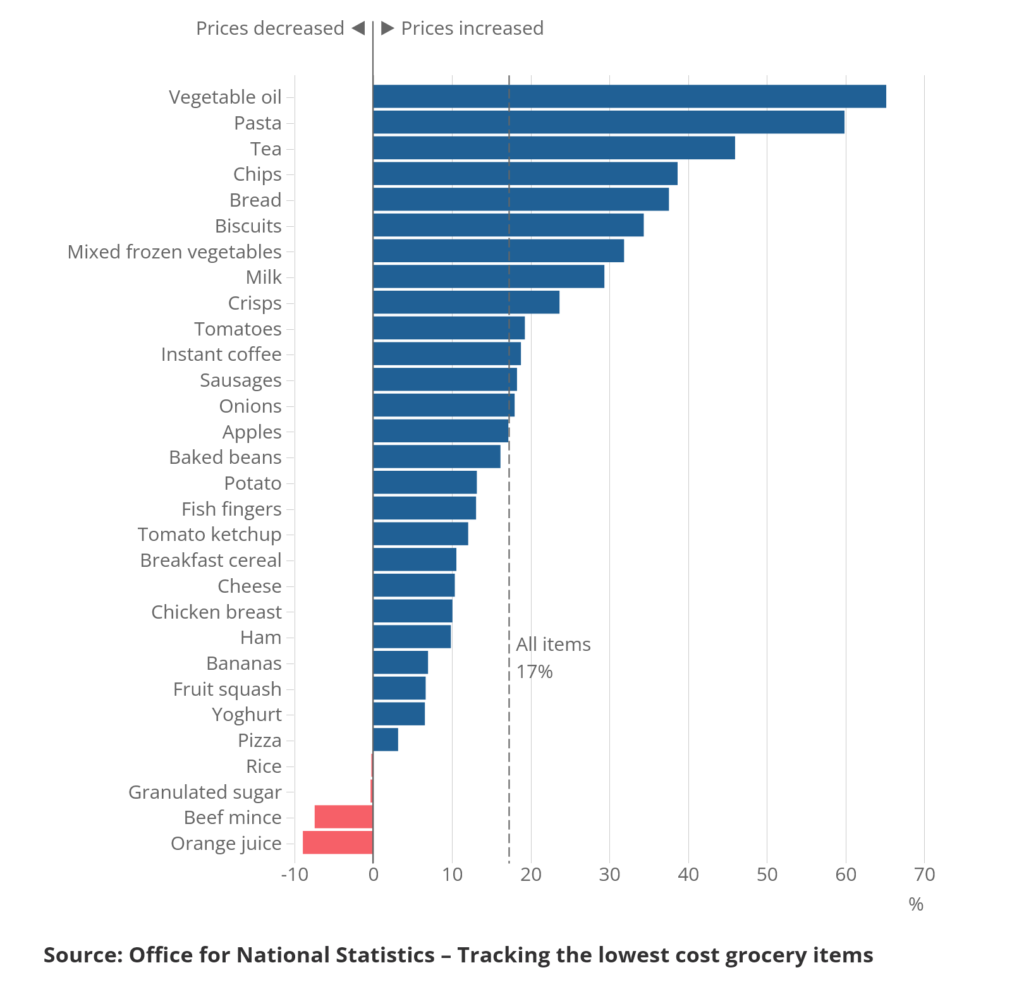
The findings of a highly untested study by the ONS (Office for National Statistics), which was derived from data scraped from the websites of 30 common grocery store items, indicate that the prices of the cheapest items have increased by approximately 17% in the 12 months leading up to September 2022, which is an increase from 7% in the 12 months leading up to April 2022.
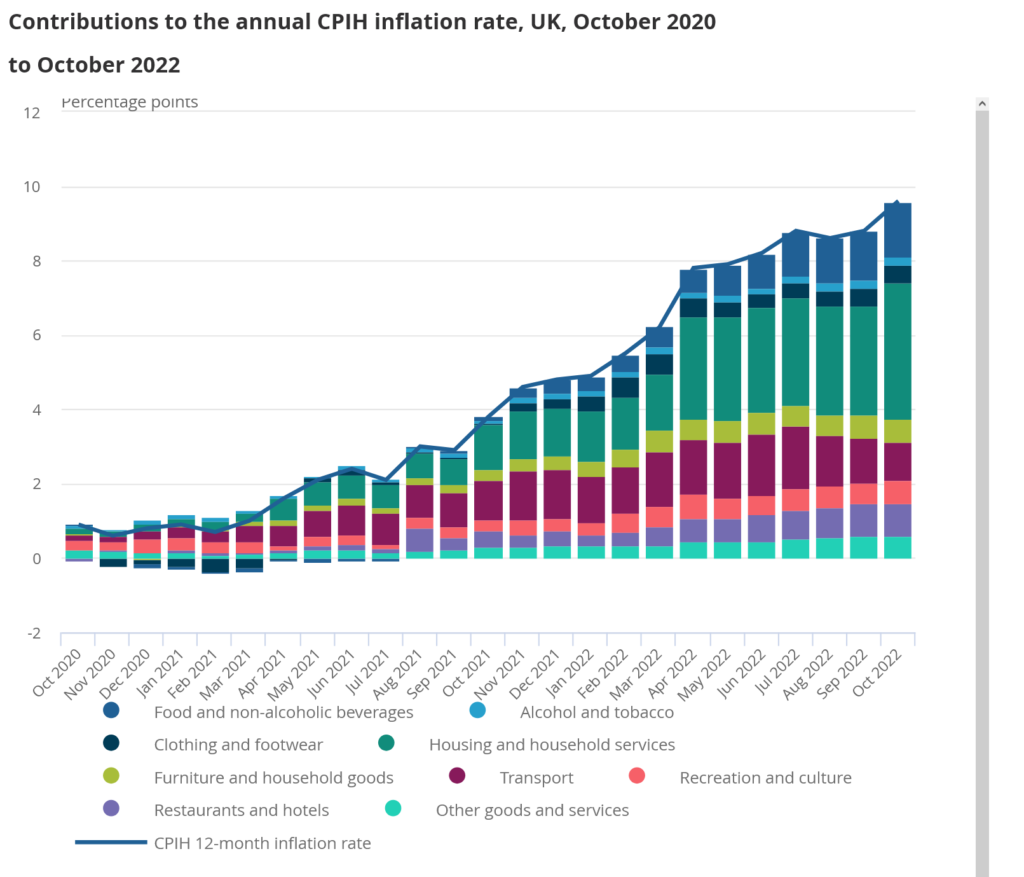
According to the statistics provided by ONS, the price of food and non-alcoholic beverages increased by 16.4% in the 12 months leading up to October 2022, which is an increase from 14.6% in September 2022. Milk, cheese, and eggs were the primary contributors to this price increase.
Prices of food and non-alcoholic beverages have been steadily increasing over the past 15 months, and it is now estimated that they have reached their highest level since September 1977, when the annual inflation rate reached 17.6 per cent.
There’s no denying that restaurant inflation is a huge problem in the UK. Inflation has been steadily increasing over the past few years, and as a result, restaurants are reporting an increase in costs for everything from food to fuel.
This means that restaurants are experiencing an increase in costs for goods and services, which can be quite burdensome for diners. This suggests that while it might be difficult for some establishments, others are able to weather these tough times by adapting their prices accordingly.
However, surprisingly, about 20% of diners typically cut spending when they encounter restaurant inflation. This means that while most people are feeling the pinch, those who frequent restaurants often have more money left over after paying their bills.
This data likely reflects how many times people visit restaurants throughout the year rather than just during high-inflation periods like right now. It’s always important to make informed decisions about where you spend your money because even small amounts can add up quickly if used regularly enough.
How Severely Will Inflation Impact Small Restaurants?
Inflation can have a severe impact on small restaurants if not managed properly. The cost of goods, as well as labour, will continue to increase, which may make it difficult for restaurateurs to keep up with the rising prices and stay in business. Additionally, increased food costs could lead diners to shift their spending away from restaurant meals and towards more affordable groceries. This would be especially true for lower-income families who depend heavily on restaurant income.
It is important for restaurateurs to monitor inflation closely and adjust their pricing accordingly so that they remain profitable while also ensuring that their customers are able or willing to pay higher prices. In some cases, this may mean closing down temporarily while other measures are put in place such as increasing wages or offering discounts on select menu items.
Inflation Restaurants
Why is it Bad for Restaurants?
As you all know from experience, rising prices always affect everyone differently – even restaurants! Most restaurateurs will tell you that when food costs go up (whether due to increased production or higher commodity prices), menu items cost more as well.
In some cases, this may be limited to specific ingredients only, while others might see broader price hikes across the board. And given that most restaurant budgets are based on fixed percentages rather than cash amounts per item, any sudden increases can quickly add up.
There are also indirect costs associated with inflation which extend far beyond just pricing strategies at the dinner table:
- wages generally don’t keep pace with inflating costs so income inequality widens; people who rely heavily on debt financing struggle more as rates rise.
Five ways in which inflation directly affects restaurants
Five ways in which inflation directly affects restaurants, and will also look at some of the indirect effects that inflation has on the industry.
- Restaurants need to increase the prices of menu items in order to cover increased costs, such as higher food safety standards, higher employee wages, and rising utility bills. Rising food costs are often seen as a greater obstacle to growth for the restaurant industry than any other cost factor.
- Higher inflation costs drive up the price of restaurant uniforms, supplies, promotional materials, and rent – all things that restaurants need to pay for even if they don’t increase their regular menu prices.
- Restaurant owners may be forced out of business if inflation hampers their ability to make a profit or pays down debts faster than they’re able to service them with interest rates at historic lows. The restaurant manager will need to monitor costs and analyse their daily, weekly and monthly figures very closely to run a very tight ship.
- Weekly specials may no longer be a profitable option for restaurants because regular customers who are used to getting certain deals will now have to pay full price for them.
- Higher household price inflation often leads consumers to dine out less at restaurants because they would rather spend their money on more essential items like groceries or shelter instead. This can lead chains that heavily rely on sales from takeout locations into difficulties concerning profitability and sustainability over time.
Positive effects of inflation on restaurant businesses?
Restaurant businesses are often at the forefront of price fluctuations, and inflation can have a positive effect on these businesses.
When prices for goods and services increase, customers tend to spend more money in order to maintain their desired level of comfort. This may mean that restaurants will see an increased demand for their products and may be able to keep up with rising costs by raising prices instead of shutting down entirely.
In fact, some restaurateurs even find that they make more money during periods of high inflation because some consumers are willing to shell out higher amounts without feeling guilty.
Inflation Trends in the UK Hospitality Industry
The hospitality industry is one of the most susceptible sectors to inflation, as prices for goods and services tend to increase over time. As a result, it’s important for restaurateurs and other operators in this sector to be aware of these trends so that they can plan their budgets accordingly. Here are some key points that you need to know about inflation and the UK hospitality industry:
- Inflationary pressures have been strongest in food services, with prices for breakfast items such as eggs skyrocketing by up to 58%. This has had a significant impact on restaurant margins as well as consumer confidence levels; people are increasingly reluctant to spend more money than necessary.
- Wage inflation has been much more gradual, with the biggest rises taking place in midrange and top-end positions. This is likely due to strong competition for these jobs and the reluctance of workers to demand pay increases that are significantly above the rate of inflation.
- Rising commodity prices have had a significant impact on hotel costs as well; items such as airfares, food services supplies, and energy bills all tend to rise faster than average when there is an increase in global economic uncertainty.
- The UK hospitality industry faces a number of direct challenges from rising inflation – including higher operating costs, reduced margins, and a heightened risk of insolvency. Restaurant operators need to be prepared for these challenges if they want to remain viable in the long term.
Overall, it’s important for restaurateurs and other operators in the UK hospitality industry to be aware of inflationary pressures and how they can impact their businesses. By planning ahead and maintaining a healthy budget, operators can help avoid any major disruptions or losses caused by inflation.
What impact do Inflationary Trends have on the Restaurant Industry?
It is always important to be aware of inflation trends and how they could potentially impact your finances. In the UK hospitality industry, these three factors are likely to have an effect on margins: Energy prices, labour costs, and Food cost inflation.
Energy prices tend to increase with increased demand globally and as a result, they account for a large portion of restaurant expenses. Labour costs are going up due to shortages in skilled personnel across the industry. And finally, food price inflation has risen steadily over the past few years owing to higher food costs and other cost increases. As a result, all three elements are contributing towards rising operational costs for restaurants.
Understanding the Drivers of Price Fluctuations
Supply Chain Disruptions
A sequence of extraordinary occurrences, such as the global COVID-19 pandemic, geopolitical tensions, and extreme weather conditions, have severely disrupted the global supply chain. These disruptions have caused delays, increased transportation costs, and shortages of essential commodities.
Increased Demand
The demand for food service products has surged as economies recover from the pandemic. Heightened demand and limited supply have led to significant price increases. Restaurants and food service providers are particularly affected as they strive to meet consumer expectations while managing costs.
Labour Shortages
Labour shortages across the food service sector have exacerbated the situation. The challenge of locating and keeping skilled workers has resulted in higher wages., further driving up operational costs. This labour crisis impacts every stage of the supply chain, from production to delivery.
Impact of Inflation on the Foodservice Sector
Rising Ingredient Costs
The increase in inflation led to a significant surge in the prices of essential ingredients like meat, dairy, and grains. This price escalation has a direct effect on menu pricing, forcing food service providers to either absorb the costs or pass them on to consumers.
Increased Operational Expenses
Beyond ingredient costs, inflation affects various operational expenses, including utilities, rent, and equipment maintenance. These increased expenses put additional financial pressure on businesses struggling with narrow profit margins.
Consumer Price Sensitivity
As prices rise, consumers become more price-sensitive, potentially reducing dining out frequency and overall spending. Food service providers must balance the need to cover costs with the risk of alienating price-conscious customers.
Diversifying Supply Sources
Food service providers should carefully consider diversifying their supply sources to reduce the dangers linked to possible disruptions in the supply chain. This means looking beyond a single supplier or region for essential ingredients. By doing so, they can create a more resilient supply chain, ensuring a steady flow of necessary items and reducing the impact of any potential disruptions on their operations.
Implementing Dynamic Pricing Models
Dynamic pricing models adjust prices based on current market conditions and can help food service providers remain competitive. Businesses can optimize pricing strategies by leveraging data analytics to reflect real-time costs and demand.
Investing in Technology
Investing in advanced technologies, such as inventory management systems and automated ordering processes, can enhance efficiency and reduce waste. These technologies enable better resource management and cost control, ultimately improving profitability.
Enhancing Labour Management
Food service providers should focus on enhancing labour management practices to address labour shortages by :
- Offering competitive wages.
- Providing training and development opportunities.
- Creating a favourable work atmosphere is crucial to maintaining a productive and harmonious workplace and to attracting and retaining skilled employees.

Related articles:
Conclusion
The food service sector faces significant challenges due to ongoing price fluctuations. Inflation can increase the cost of goods that are used in restaurants. This can lead to margin pressure on restaurant managers and owners. However, there are some strategies that they may be able to use to combat this pressure – such as price increases or introducing new menu items at a higher price point.
As a restaurant owners you can navigate the inflation effect on your restaurant effectively by understanding the underlying drivers and implementing strategic measures. Diversifying supply sources, adopting dynamic pricing models, investing in technology, and improving labour management are critical steps towards ensuring sustainability and profitability in this volatile economic landscape.
In the end, it is time to assess whether you should cut down on your costs and increase the prices of your menu items or start adapting to new ways of doing things. If the cost of ingredients keeps rising, restaurants will be forced to ensure that their customers get value for every penny spent.
In order to stay ahead in times like these, it’s important for all restaurant businesses – from small cafes to big chains –to prepare for and manage inflation effectively. This requires not only having a strong pricing strategy but also understanding how your customer base deals with changes in cost.
By getting early indications about what people are willing to pay and how quickly they’re adjusting their spending habits (for instance by launching more affordable promotions), you can make the right decisions today so that you have a healthy bottom line tomorrow as well!
Restaurant managers and owners must stay informed about market trends and continuously adapt to changing conditions as we move forward. By doing so, the industry can survive and thrive amidst the complexities of price fluctuations and inflation.
How Much Energy Consumption An Average Restaurant Uses Every Year UK
FAQ’s
How will inflation affect restaurants?
Inflation can have several significant effects on restaurants. Firstly, the cost of ingredients and supplies will rise, leading to higher operational expenses, which can squeeze profit margins, especially for restaurants that rely heavily on fresh produce, meat, and other perishable goods. Moreover, labour expenses may rise as workers seek higher pay to cope with the increasing cost of living. Utilities and rent may also become more expensive, adding further financial pressure. As a result, restaurants might need to adjust their pricing strategies, reduce portion sizes, and most importantly, explore efficient cost-cutting measures to maintain profitability in the face of inflation.
What impacts does inflation have on food prices?
Inflation generally leads to an increase in food prices because the costs of raw materials, transportation, and labour used in food production and distribution rise. For example, higher fuel prices can make transporting goods more expensive, which raises the price of those goods. Similarly, if the cost of fertilizers, seeds, or livestock feed goes up, these higher production costs are passed along the supply chain, resulting in more expensive food items for consumers. These price hikes can affect all levels of food purchasing, from wholesale to retail.
How does inflation affect businesses?
Inflation affects businesses by increasing their goods, services, and labour costs. Companies might face higher expenses for raw materials, manufacturing, and transportation. Companies might raise their prices to manage the escalating costs. However, this could reduce consumer spending as customers adjust to the higher prices. Additionally, businesses might experience increased borrowing costs if interest rates rise to combat inflation. Inflation can also create uncertainty, making it harder for businesses to plan long-term investments and budgeting. Maintaining profitability and managing cash flow becomes more challenging in an inflationary environment.
What impact does inflation have on menu cost?
Inflation can significantly impact menu costs in restaurants. As the prices of ingredients rise, restaurants need to adjust their menus to reflect these increased costs. This often results in higher prices for menu items. However, it’s crucial for restaurants to balance price increases with customer retention, as drastic price hikes can deter patrons. Some restaurants may opt for smaller portion sizes or use lower-cost ingredients to maintain menu prices. Additionally, inflation can lead to more frequent menu updates to keep pace with fluctuating costs, which can increase administrative work and printing expenses. Overall, maintaining a profitable yet appealing menu becomes more complex during inflationary periods.


